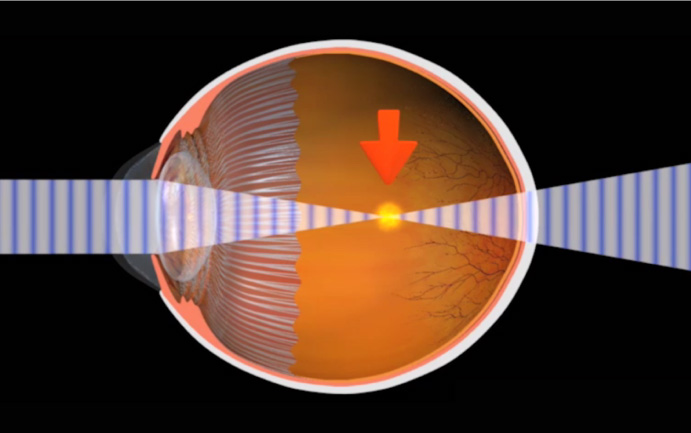
Myopia is the condition of being nearsighted. When it is an inherited condition, myopia begins early in life. People with this condition can usually see near objects, but they struggle to see distant objects. Myopia is the opposite of hyperopia, or farsightedness. In myopia, the anatomy of the eyeball, or globe, is longer than normal. This causes the light to focus in front of the retina, blurring the distance vision. Myopia is corrected with glasses and contact lenses, or with laser vision correction. Laser vision correction is only recommended for people over 18 years old, when the eye has finished growing to adult size.
To correct the symptoms of myopia with glasses, lenses are used that are thicker on the edges and thinner in the middle. This is known as a concave lens, which can be cosmetically improved in higher prescriptions with a high index lens.
Myopes are also at increased risk for a retinal detachment. The signs and symptoms of a retinal detachment are flashing lights, black floaters, or a curtain over the vision. The risk of detachment is typically less than 3 percent.